- cross-posted to:
- hackernews@lemmy.smeargle.fans
- cross-posted to:
- hackernews@lemmy.smeargle.fans
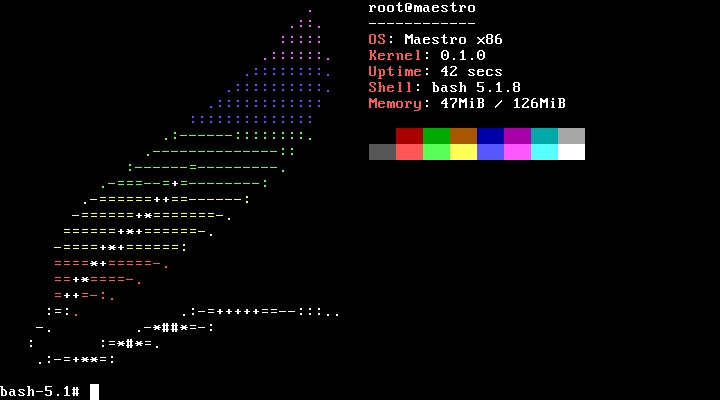
Enter Maestro, a unix-like monolithic kernel that aims to be compatible with Linux in order to ensure wide compatibility. Interestingly, it is written in Rust. It includes Solfége, a boot system and daemon manager, maestro-utils, which is a collection of system utility commands, and blimp, a package manager. According to Luc, it’s creator, the following third-party software has been tested and is working on the OS: musl (C standard library), bash, Some GNU coreutils commands such as ls, cat, mkdir, rm, rmdir, uname, whoami, etc… neofetch (a patched version, since the original neofetch does not know about the OS). If you want to test it out, fire up a VM with at least 1 GB of ram.
This sounds cool, but troubling because of its license. Trying to write a linux compatible kernel and licensing as MIT is basically asking to get railroaded by gigantic organizations. I hope they reconsider in the future.
because of its* license
Thanks :)
deleted by creator
deleted by creator
Its a bit if an issue with the rust ecosystem in general tbh. Wish more stuff was copyleft >.<
Could someone detail why? Why is MIT license troublibg?
MIT is basically “do anything you want with it, I don’t care”. I means some company can reuse it in its closed source projects freely and without notice or royalty.
There are plenty of other licenses that require you to also go open source if you include and/or modify it. Basically “you can use ot however you want, but if you modify it, it has to be open source as well”
According to Luc, its* creator
Username checks out
N O T I T S
Username checks out?
I think that’d be sugar chest
BUT WHAT WE MAKE
It snot its
Keep fighting the good fight. Syntax is important.
Yes. Thank you, “It’s no tits”!
Ok, I’m out of the loop and I’ve seen this often enough that I have to ask; why do people always bring up “written in rust”? No one points out that a given project is written in C++/C#/python/ruby etc, yet we keep seeing it for rust.
If you want a real answer, it’s mostly advocacy, the same reason Linux enthusiasts show up to every negative-sounding Windows thread to tell you to install Linux instead. And if it is less obnoxious, it’s only because there’s fewer Rust enthusiasts.
There are, also, advantages to a Rust implementation that you can claim simply by virtue of something being implemented in Rust, as entire categories of problem that cause C projects to hemorrhage security vulnerabilities simply don’t exist for Rust.
But mostly it’s people wanting you to be excited about and interested in Rust.
Is there something inherently safer with how rust does things, or is it just a case of it being new, so the vulnerabilities haven’t been found yet?
Yes, it is inherently safer than C. Unless you write code in an
unsafeblock, Rust will handle many aspects of memory allocation and management for you, and ensure their safety. It is memory safe and thread safe by default.C doesn’t have any of these safety checking features, so it would be equivalent to unsafe Rust, but all the time. It lets you do whatever you want with pointers for example, including making them point outside of the memory bounds. In program code, this will cause an illegal memory access exception, but in kernel code, all memory access is legal. Therefore, you could write a driver that accidentally overwrites the kernel’s own code in memory. That would likely cause a kernel panic and bring the whole system down. Whereas, in Rust, you can only do that within an
unsafecode block.Here’s the summary for the wikipedia article you mentioned in your comment:
Thread safety is a computer programming concept applicable to multi-threaded code. Thread-safe code only manipulates shared data structures in a manner that ensures that all threads behave properly and fulfill their design specifications without unintended interaction. There are various strategies for making thread-safe data structures.A program may execute code in several threads simultaneously in a shared address space where each of those threads has access to virtually all of the memory of every other thread. Thread safety is a property that allows code to run in multithreaded environments by re-establishing some of the correspondences between the actual flow of control and the text of the program, by means of synchronization.
I only know the hype. But the hype says that Rust’s ownership system makes memory usage much safer by forcing the coder to deal with data. Your values will eventually go out of scope, and you have to dictate when that will happen or else it won’t compile.
…or something like that.
deleted by creator
deleted by creator
I feel like this is an example of innovation vs invention. Rust did not invent borrow checking. It did, however, make the borrow checker an integral part of the language and compiler. Making memory safety the default behavior is innovative and makes it the path of least resistance.
Memory safety issues are responsible not just for crashes and perf degredation but are a significant attack vector for exploits. Making it harder to land there makes these exploitable conditions less common. The mechanism is not unique but its integral place in the language is.
It kinda really pioneered its particular kind of memory management. There’s some theoretical ancestry involving ML-based research languages with region typing, stuff like this, but those are ultimately quite different. The rest of the type system is basically a cut-down Haskell (Hindley-Milner with qualified types (typeclasses/traits)), with some minor titbits and fiddling.
deleted by creator
Borrow checking is part of the language specification, and a compiler that does not include it is, by definition, incomplete. The authors of mrust even state this in the project README.
Your claim is roughly equivalent to saying a C compiler which does not produce an error when a program calls an undeclared function means that C as a language does not ensure that your code doesn’t call functions that don’t exist - i.e., nonsense at worst, and irrelevant at best.
But it also has a cool name. You forgot to mention that very important aspect.
Because rust is the modern low level systems language, which means it gotta go fast without all the freaking problems of the only other real alternative so far that was C. The languages you list don’t even play in the same ballpark.
But a kernel written in Perl would be a real achievement. Something in a whole different league.
It definitely would be. Next time someone posts a kernel written in Perl I hope they specify that.
Pernel
Honest question from someone using C++, though not for systems- or embedded stuff, just for object oriented models that gotta go fast: Why is C++ not in the same ballpark, and not an alternative?
Mentioning it’s written in rust should imply this code base will have secure concurrency, better memory handling, be easier to extend, while maintaining near C++ performance. None of these are guarantees, but considering so many rust projects are “C/C++ programs, rewritten” it seems worth calling out as a differential. The language’s advantages extending to the kernel make it an interesting project.
Yes they do? All the time? To the point where github has a bar on every project page showing what percentages of every project is written in which languages?
deleted by creator
Started as a school project
I wouldn’t take it so seriously, it’s a passion project from a person learning about Rust and OS structure. Don’t compare this project against industry professionals.
Why not ? Even Linux started as a personal fun project. Let’s see where it will go
For sure, but making an OS is not a one man job anymore.
Bah gaw. Terry Davis would say you “glow in the dark.”
I knew there would be at least one TempleOS reference in this thread lmao
Finally, some “exciting” news, 2031 will be the year of the linux desktop(and Maestro)!
It’s interesting, but with Linux and BSD already available in many different flavours do we really need it?
I mean what use case would it be better in except maybe an extreme rust enthusiast.
do we really need it?
Asked no programmer ever before starting a project
If it’s cool (as this is), then yes. It’s needed :-)
It isn’t needed to be required for one to like developing it.
With minix already available I see no reason why we need a Linux kernel
Whats the need for it? Another great operating systems engineer emerging from it even though the project itself might not be ‘useful’. You only truly learn stuff when actively doing it.
One day he might be a significant contributor to Linux!
But, but… rust?!!
- Memory safety is super important
- Rust is far more approachable than C, so contribution and iteration is easier
- Did we really need an OS when Linux was released? It wasn’t the first.
It was the first fully working kernel licenced under a FOSS licence. So it was the first time someone could run a 100% open source OS.
At least since maybe some really old mainframe back when stuff came with source code
it’s not that everybody should work solely on what you deem useful/needed, eh
deleted by creator
A VM with 1GB of RAM but the screenshot shows 50MB in use?
Oh, looks like the install live environment needs it.
You should’ve read the article, ”You should run the ISO with sufficient RAM (1GB should be more than enough). Such an amount of memory is required because packages to be installed are stored in RAM (on the initramsfs) instead of the disk. This is currently the best method since the OS is not yet able to read on a USB stick or CD-ROM by itself, so it relies on the bootloader for this. ”
I guess you could run on lower ram, but package installs require more.
I did read the article, reason of my edit
Why?
Because someone decided to do it.
You don’t always need a good reason other than it might be cool/fun. Sometimes it’s just because you can.
You’re not forced to use it, so if it’s not your cup of tea, that’s fine.
When my wife asks me “why are you doing [insert weird thing of the moment in my homelab]?” most of the times I answer “because I can!”.
When my wife asks me “why are you doing [insert weird thing of the moment in my homelab]?” most of the times I answer “because I can!”.
Exactly!
He answers that in the project page. Just because there are kernels available, he can’t build his own and learn about kernel and computers in general (the answer for your question)