Researchers have devised an attack that forces Apple’s Safari browser to divulge passwords, Gmail message content, and other secrets by exploiting a side channel vulnerability in the A- and M-series CPUs running modern iOS and macOS devices.
iLeakage, as the academic researchers have named the attack, is practical and requires minimal resources to carry out. It does, however, require extensive reverse-engineering of Apple hardware and significant expertise in exploiting a class of vulnerability known as a side channel, which leaks secrets based on clues left in electromagnetic emanations, data caches, or other manifestations of a targeted system. The side channel in this case is speculative execution, a performance enhancement feature found in modern CPUs that has formed the basis of a wide corpus of attacks in recent years. The nearly endless stream of exploit variants has left chip makers—primarily Intel and, to a lesser extent, AMD—scrambling to devise mitigations.
. . .
While iLeakage works against Macs only when running Safari, iPhones and iPads can be attacked when running any browser because they’re all based on Apple’s WebKit browser engine.
Member how Apple argues ((security)) to justify their monopoly enforcement of WebKit on iOS? Lol. Good one.
Of course they bury the important bit right at the end of the article:
“There’s no indication that this vulnerability has ever been discovered before, let alone actively exploited in the wild.
That means the chances of this vulnerability being used in real-world attacks anytime soon are slim, if not next to zero. It’s likely that Apple’s scheduled fix will be in place long before an iLeakage-style attack site does become viable.”
Streisand effect, anyone?
I would have said yes-card effect.
This is the best summary I could come up with:
Researchers have devised an attack that forces Apple’s Safari browser to divulge passwords, Gmail message content, and other secrets by exploiting a side channel vulnerability in the A- and M-series CPUs running modern iOS and macOS devices.
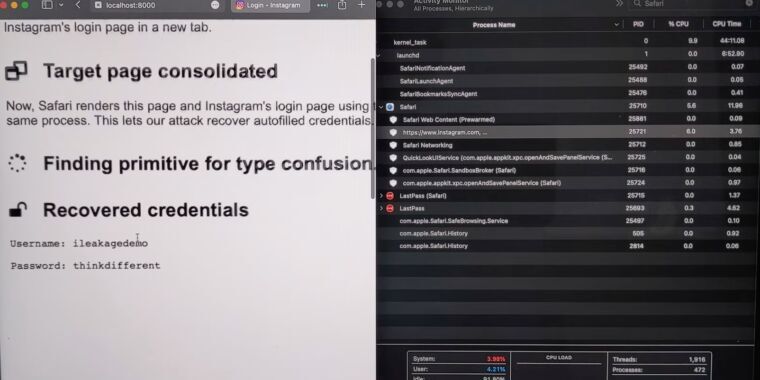
The researchers have successfully leveraged iLeakage to recover YouTube viewing history, the content of a Gmail inbox—when a target is logged in—and a password as it’s being autofilled by a credential manager.
Once visited, the iLeakage site requires about five minutes to profile the target machine and, on average, roughly another 30 seconds to extract a 512-bit secret, such as a 64-character string.
“In particular, we demonstrate how Safari allows a malicious webpage to recover secrets from popular high-value targets, such as Gmail inbox content.
Finally, we demonstrate the recovery of passwords, in case these are autofilled by credential managers.”
The design of A-series and M-series silicon—the first generation of Apple-designed CPUs for iOS and macOS devices respectively—is the other.
The original article contains 327 words, the summary contains 157 words. Saved 52%. I’m a bot and I’m open source!